Active Transport Could Best Be Described as
Terms in this set 12 Which of the following is true regarding active transport. Active transport mechanisms collectively called pumps work against electrochemical gradients.
Difference Between Active And Passive Transport Definition Types How It Works
There are two types of active transport.

. Sodium moving out of the cell against its concentration gradient. To learn more about the transport cells review the corresponding lesson on Passive and Active Transport in Cells. Part 15 Active transport can best be described as Multiple Choice the diffusion of water from areas where water concentration is higher to areas where water concentration is lower.
It involves using energy usually ATP to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. Active Transport involves the movement of solutes against a concentration gradient that is from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cells energy usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP.
Active transport is a process that is required to move molecules against a concentration gradientThe process requires energy. Active transport is responsible for bidirectional movement of the majority of macromolecules 60 kDa as well as for transport of smaller proteins that possess a nuclear import NLS or export NES signal Gorlich and Mattaj 1996. Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration against the concentration gradient.
Biology questions and answers. Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy while active transport requires energy to get done. Active transport is a way for molecules to move across the plasma membrane.
Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein using energy supplied by ATP. All nuclear proteins are imported from the cytoplasm their site of synthesis to. Which of the following is an example of active transport in a cell.
If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient that is if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid the cell must use energy to move the. In this kind of biochemical transport large and heavy molecules of food and waste are forcefully moved in and out of the cell body with the help of pumping that requires energy. The movement of molecules with their concentration gradient from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
The movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane in the direction opposite that of diffusion that is from an area of lower concentration to one of higher concentration. Thus this is an important process in cell biology that requires energy. There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used.
For a charged solute it is movement against the combination of concentration and electrical. Active transport in plants. Movement Across a Membrane and Energy.
Active transport mechanisms do just this expending energy often in the form of ATP to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in. To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy.
Primary and Secondary active transport. Secondary active transport is a form of active transport across a biological membrane in which a transporter protein couples the movement of an ion typically Na or H down its electrochemical gradient to the uphill movement of another molecule or ion against a concentrationelectrochemical gradient. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes.
Active transport process is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient ie moving from a lower to higher concentration. Active Transport is the biological body transport system that does not follow the natural phenomena of transport. A gradient produced by the combined forces of the electrical gradient and the chemical gradient.
Cartoon representing passive transport as rolling a boulder. When active transport is used to move molecules what is required. Secondary Active Transport.
It occurs against the concentration gradient. Substances that are transported across the cell membrane by primary active transport include metal ions such as Na K Mg2 and Ca2. Up its concentration gradient that is from a low concentration to a high one.
Active transport is the term reserved for transport processes that result in the movement of a solute uphill or against its natural direction. Identify the two main ways substances get moved. Active transport is the movement of particles through the cellular membrane against their concentration gradient.
Thus energy stored in the. A type of active transport that moves substances including fluids and particles into a cell. Which of the following cell transport processes would be most negatively impacted if.
For the case of a neutral solute at constant temperature and pressure this resolves into movement against a concentration difference. Primary active transport is also called direct active transport or uniport. This lesson will help you.
Active transport moves a solute. Cole and Hammel 1998. Moving against a gradient.
Corbett and Silver 1997. A carrier protein on the surface of the cell. The method of transporting material that requires energy.
Endocytosis relies on active transport. Active and passive transport are biological processes that move oxygen water and nutrients into cells and remove waste productsActive transport requires chemical energy because it is the movement of biochemicals from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. Active transport uses cellular energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Primary active transport involves the role of sodium. This type of molecular movement is called uphill movement and requires expenditure of energy. Definition of active transport.

Passive And Active Cell Transport Word Wall Cards Diffusion And Osmosis Etc Biology Lessons Teaching Biology Study Biology

Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
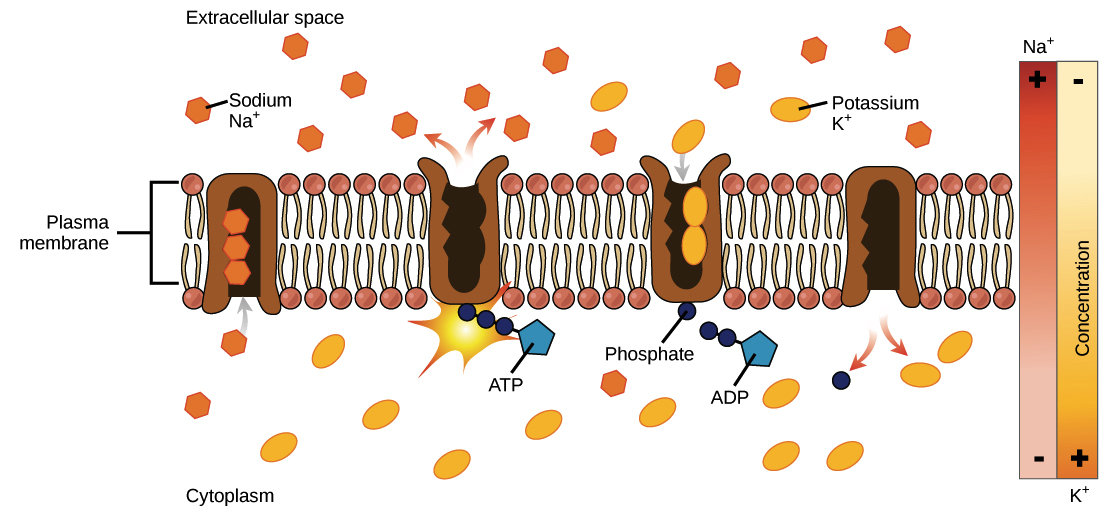
Active Transport Review Article Khan Academy

Examples Of Active Transport In Plants And Animals

Passive Transport And Active Transport Across A Cell Membrane Article Article Khan Academy

Active Transport Features Types And Significance
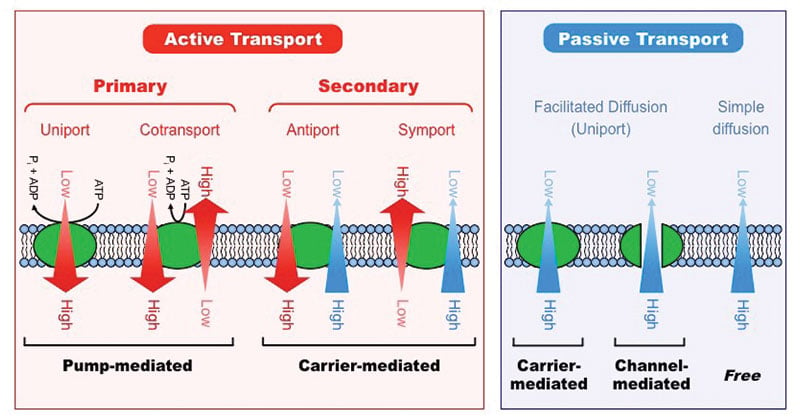
Active Vs Passive Transport Definition 18 Differences Examples
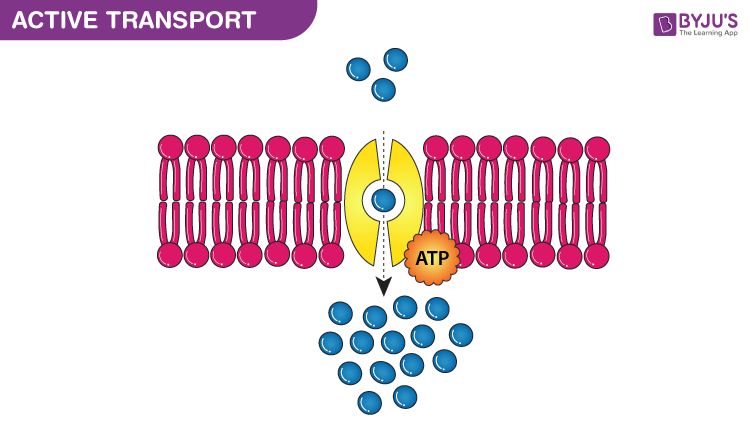
Active Transport Definition And Types Of Active Transport
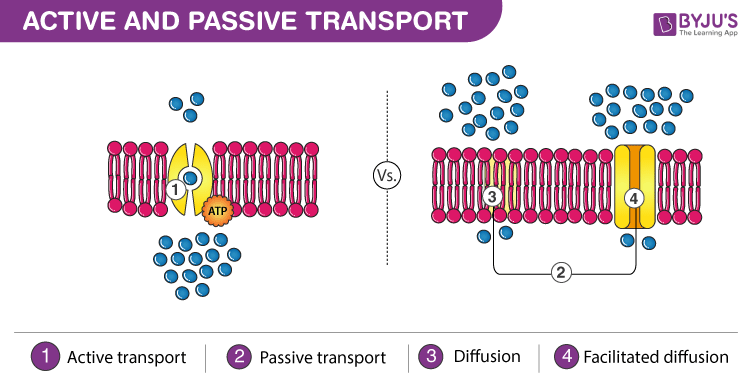
Difference Between Active Transport And Passive Transport
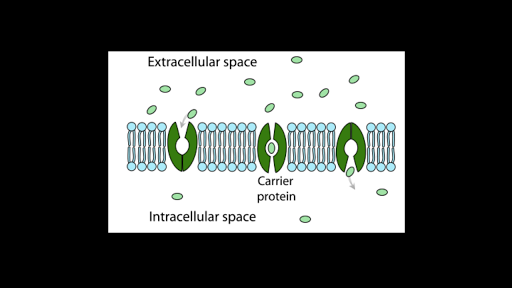
Simple Diffusion And Passive Transport Article Khan Academy
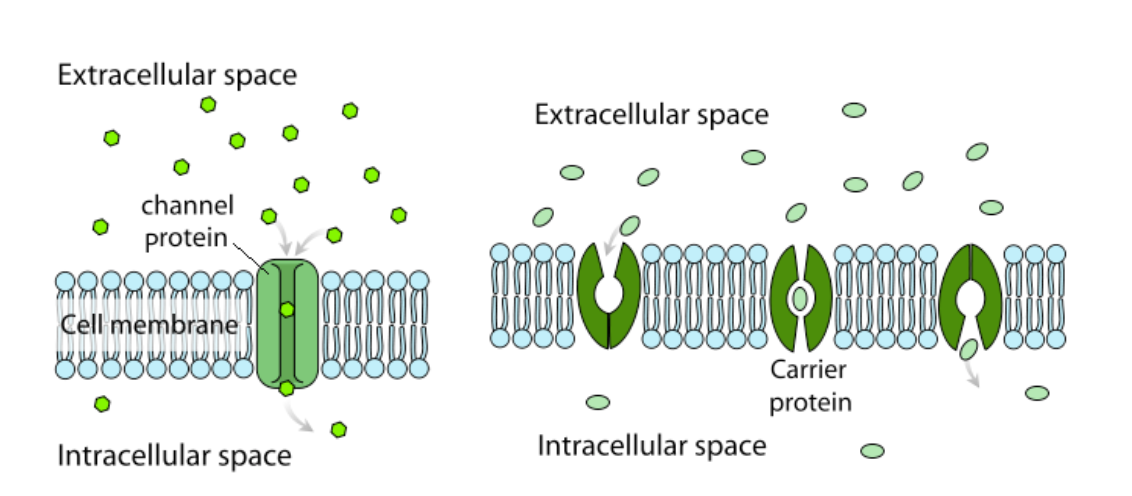
Passive Transport Review Article Khan Academy

Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Passive Transport And Active Transport Across A Cell Membrane Article Article Khan Academy

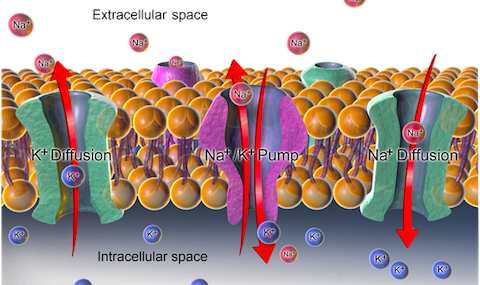
5 3c Secondary Active Transport Biology Libretexts
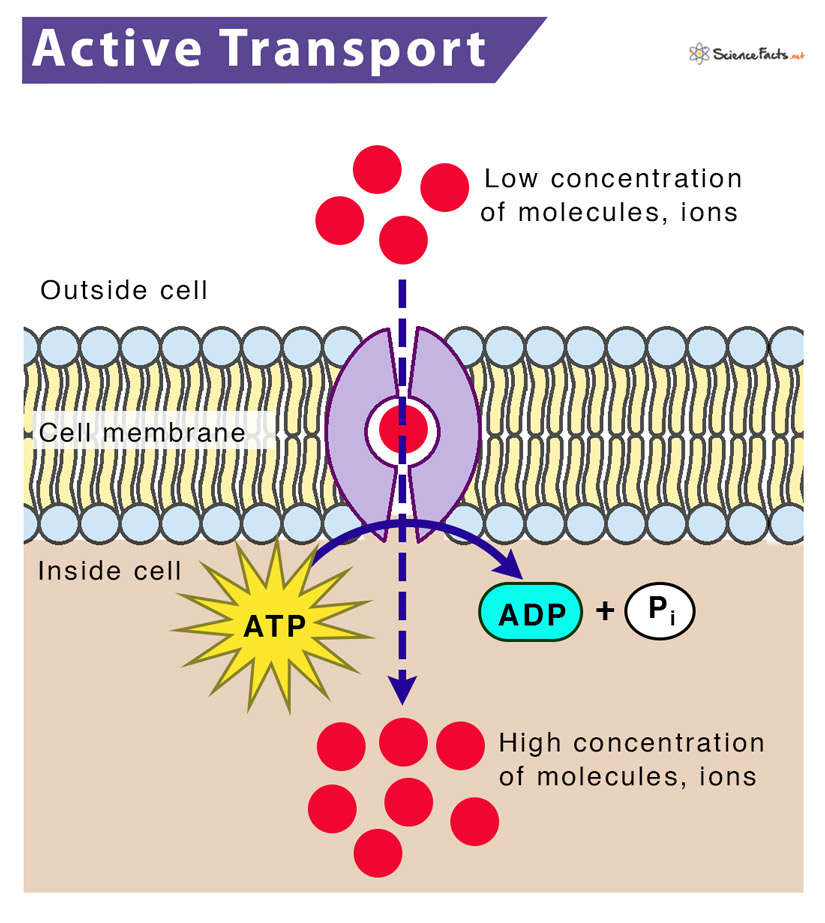
Active Transport Definition Types Functions And Diagram
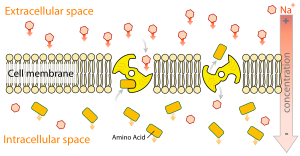
Secondary Active Transport Wikilectures

Passive Vs Active Transport Membrana Celular Ap Biology Transporte Passivo

Comments
Post a Comment